Aaron Jackson
Ovarian Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries, the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs. These cysts are quite common, affecting many women during their childbearing years.
This article aims to be your comprehensive guide to ovarian cysts. We'll delve into the different types of cysts, explore the causes and risk factors, shed light on the potential symptoms, and discuss the various treatment options available.
Understanding the Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are several types of ovarian cysts, each categorized based on their origin and composition. Here's a breakdown of the most common types:
- Functional cysts: These are the most frequent type, typically harmless, and often disappear on their own within a few menstrual cycles.
- Follicle cyst: This arises from a developing egg follicle that fails to rupture during ovulation.
- Corpus luteum cyst: This forms from the remaining follicle after ovulation but doesn't dissolve as expected.
- Endometriomas: These occur in women with endometriosis, a condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus. They can be painful and persistent.
- Dermoid cysts: These contain a mixture of tissues like hair, skin, or teeth – remnants of the fetus during development. They are uncommon but can grow large.
- Cystadenomas: These are benign epithelial tumors that can be serous (fluid-filled), mucinous (mucus-filled), or cystadenofibroma (a mix of both).
Unveiling the Causes of Ovarian Cysts
While the exact cause of ovarian cysts remains unclear, several factors can contribute to their development:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Ovulation, pregnancy, and hormonal imbalances can trigger cyst formation.
- Endometriosis: As mentioned earlier, this condition can lead to endometriomas.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This infection can spread to the ovaries and cause cysts.
- Genetics: Some women may have a genetic predisposition to developing cysts.
- Past ovarian surgeries: Prior surgeries on the ovaries can increase the risk.
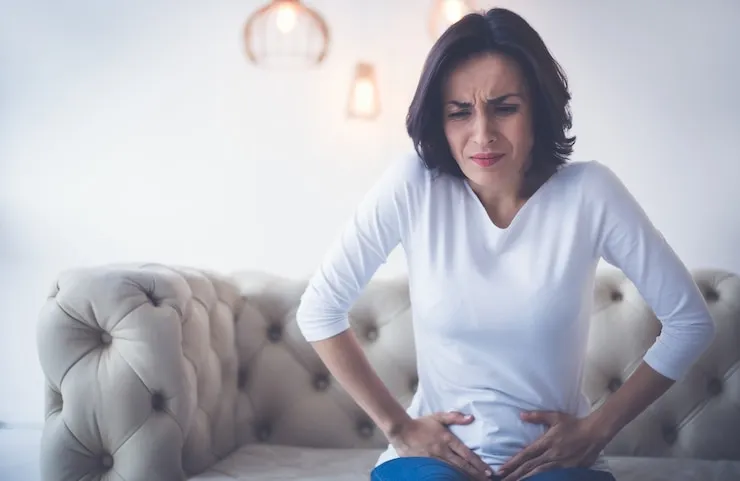
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, meaning they don't cause any noticeable symptoms. However, larger cysts or those that rupture, bleed, or twist the ovary can cause the following:
- Pelvic pain: This can be a dull ache or a sharp pain on one side of the lower abdomen.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen is a common symptom.
- Painful intercourse: Sexual activity can be uncomfortable if a cyst is present.
- Irregular menstrual periods: Changes in bleeding patterns, heavier periods, or spotting between periods can occur.
- Urinary urgency or frequency: Pressure from a cyst can affect bladder function.
- Painful bowel movements: Similar to urinary issues, a cyst can impact bowel function.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can occur if a cyst ruptures or twists the ovary.
- Sudden and severe abdominal pain: This could indicate a ruptured cyst and requires immediate medical attention.
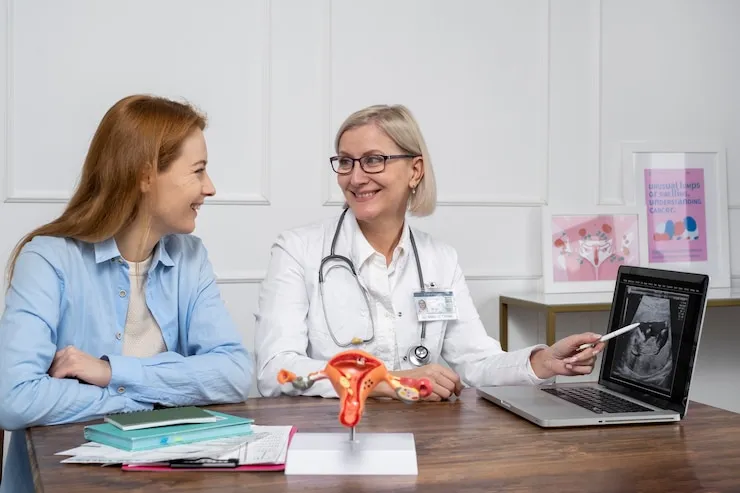

When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms, especially if they are severe or persistent, consult a doctor:
- Pelvic pain, especially if it worsens or interferes with daily activities
- Sudden and severe abdominal pain
- Heavy bleeding or irregular periods
- Fever or nausea with severe pain
- Difficulty emptying your bladder or bowels
Exploring Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts
The treatment approach for ovarian cysts depends on several factors, including the type, size, and presence of symptoms. Here's a breakdown of the common treatment options:
- Monitoring: For small, asymptomatic cysts, doctors often recommend watchful waiting, monitoring the cyst through regular pelvic exams and ultrasounds to ensure it doesn't grow or cause problems.
- Hormonal birth control: Birth control pills can help regulate ovulation and prevent the formation of new functional cysts.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the cyst, especially if it's large, causing symptoms, or suspected to be cancerous. There are several surgical approaches:
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure using a small incision and a laparoscope (a viewing instrument) to remove the cyst.
Laparotomy: A traditional open abdominal surgery performed for larger or complex cysts.
Cystectomy: This surgery removes the cyst while preserving healthy ovarian tissue.
Oophorectomy: In some cases, the entire ovary may need to be removed, particularly if the cyst is cancerous.

Recovery and Post-Treatment Care
Recovery from ovarian cyst treatment varies depending on the type of surgery performed.
- Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive approach typically involves a short hospital stay (often same-day) and recovery within a week or two. You might experience some soreness around the incision sites and fatigue. Rest is crucial for proper healing. Resuming normal activities can be gradual, with lifting restrictions for several weeks.
- Laparotomy: As a more invasive surgery, recovery from a laparotomy takes longer, with a hospital stay of a few days and a complete recovery period of up to eight weeks. You can expect more pain and discomfort compared to laparoscopy. Following your doctor's instructions on activity restrictions, pain management, and wound care is essential.
Living with Ovarian Cysts
For women with diagnosed ovarian cysts, regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are crucial. This allows them to monitor the cyst and identify any changes or potential complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also be beneficial:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts.
- Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote overall health.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help manage weight and improve overall well-being.
- Managing stress: Stress can affect hormonal balance, potentially contributing to cyst formation. Techniques like yoga or meditation can be helpful.
Emotional Impact and Support
A diagnosis of an ovarian cyst can be emotionally challenging, especially if surgery is needed. It's normal to experience anxiety or fear about the outcome. Here are some tips for managing your emotional well-being:
- Communicate openly with your doctor: Ask questions and address any concerns you have.
- Seek support from loved ones: Talk to your family and friends about your experience.
- Consider joining a support group: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can be helpful.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness meditation can help manage stress and anxiety.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are a common occurrence, and most are harmless and resolve on their own. However, understanding the different types, potential causes, and symptoms can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Early detection and appropriate treatment are key to managing ovarian cysts and ensuring your overall well-being. If you have any concerns about ovarian cysts, don't hesitate to talk to your doctor.

 Telehealth Visits Available
Telehealth Visits Available