15 Nov 2022 | Aaron Jackson
What causes Scoliosis?
An abnormal lateral curving of the spine is called scoliosis. The most typical time for a diagnosis is in early adolescence or childhood. The cervical, thoracic, and lumbar areas, together referred to as the "sagittal plane," are where the spine normally curves. These natural curves position the head above the pelvis and act as shock absorbers to distribute mechanical stress during exercise. The curvature of the spine in the "coronal" (frontal) plane is a common definition of scoliosis. Although the degree of curvature is measured at the coronal level, scoliosis is actually a more complex, three-dimensional problem that affects the following planes :-
- Coronal plane
- Sagittal plane
- Axial plane
The coronal plane is a vertical plane parallel to the shoulders, from head to toe, that divides the body into anterior (anterior) and posterior (posterior) sections. The sagittal plane splits the body from left to right. The axial plane is parallel to the ground and perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes.

Where can you get better treatments for Scoliosis?
- Dallas Back Clinics specialize in surgical and non-surgical treatment of back pain, and spinal disorders.
- If you are seeking treatment for scoliosis and other spinal conditions you are at the right place.
- Our team of experienced healthcare professionals cares for all your spine-related problems including scoliosis.
- At Dallas Back Clinics , from degenerative disorders to spinal deformities or sudden injuries, our top doctors perform some of the most advanced and complex procedures.
- If you find any symptoms of scoliosis, seek medical care as soon as possible to avoid severe conditions.
- For a better treatment of the spine, visit Dallas Back Clinics website’s homepage or call 469-833-2927 and book an appointment.
What are the signs and symptoms of Scoliosis?
- Uneven shoulders.
- The head is not directly above the pelvis.
- One or both hips are elevated, or the rib cages are exceptionally high.
- Uneven waist.
- The skin that covers the spine changes in appearance or texture (dimples, hairy patches, colour abnormalities).
- The whole body tilts to one side.

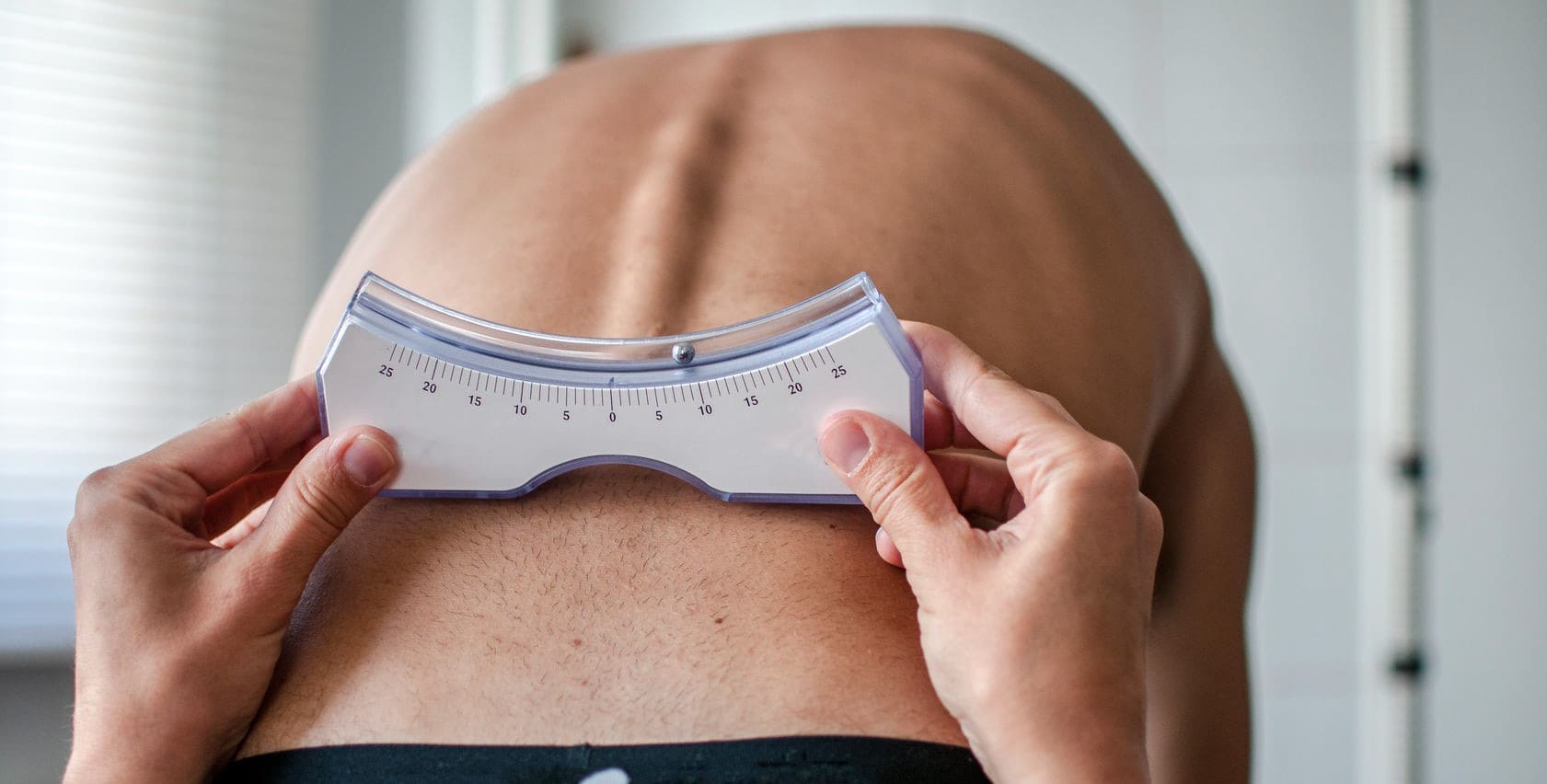
In what ways Scoliosis can be Diagnosed?
- X-ray :- When radiation is used to create a film or image of a bodily component, the vertebral structure and the location of the joints may be seen. To look for further potential sources of pain, such as infections, fractures, abnormalities, etc., X-rays of the spine are taken.
- Computed tomography scan (CT or CAT scan) :- A diagnostic picture produced by a computer after reading X-rays can display the size and form of the spinal canal, as well as the contents and structures around it. Excellent at visualizing skeletal structures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) :- A diagnostic procedure that uses strong magnets and computer technology to create three-dimensional photographs of bodily parts. It can reveal enlargements, degeneration, and abnormalities of the spinal cord, nerve roots, and their surroundings.
Scoliosis is easy to treat when it is diagnosed early. In many cases, scoliosis does not need treatment. For moderate to severe cases, treatment can help prevent scoliosis from worsening and relieve other symptoms.
How to treat Scoliosis?
Following a scoliosis diagnosis, it is important to evaluate a number of factors that might influence the available treatment choices.
- Does the patient's spine still develop and change as they age?
- The severity of the curve and how it affects the patient's lifestyle depend on its degree and extent.
- Location of the curve.
- Curve progression is a possibility, and it is more likely to occur in kids who have big curves before their teenage growth spurts.
Following the evaluation of these factors, the following therapeutic strategies could be suggested :-
- Observation
- Bracing
- Surgery
What are the causes of Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is classified by etiology, that is idiopathic, congenital, or neuromuscular.Idiopathic scoliosis is diagnosed when all other causes are ruled out and account for approximately 80% of all cases. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is the most common form of scoliosis and is usually diagnosed during puberty.
Congenital scoliosis can affect any part of the spine and is caused by the embryological abnormality of one or more vertebrae. Due to the vertebral anomalies, one part of the spinal column lengthens more slowly than the other, resulting in curvature and other malformations of the spine. The pace at which the child's scoliosis increases in severity as they become older depends on the geometry and placement of the anomalies. Congenital scoliosis is often found earlier than idiopathic scoliosis since these anomalies are evident at birth.
Neuromuscular scoliosis includes scoliosis secondary to neuropathy or muscle damage. These include cerebral palsy, spinal cord trauma, muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, and scoliosis associated with spina bifida. This type of scoliosis generally progresses more quickly than idiopathic scoliosis and often requires surgical treatment.
What are the complications of scoliosis?
Scoliosis often affects people in a minor form, however, it can occasionally result in issues such as :-
- Breathing problems :- When scoliosis is severe, the rib cage may press on the lungs, making breathing more challenging.
- Back problems :- Especially if the abnormal curves are significant and untreated, individuals who experienced scoliosis as children may be more prone to experience persistent back discomfort.
- Appearance :- Scoliosis can lead to increasingly obvious abnormalities as it progresses, such as lopsided hips and shoulders, protruding ribs, and a tilting of the waist and trunk to one side. Scoliosis sufferers frequently feel self-conscious about their looks.

 Telehealth Visits Available
Telehealth Visits Available