02 Jan 2023 | Jennifer
What Causes Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy?
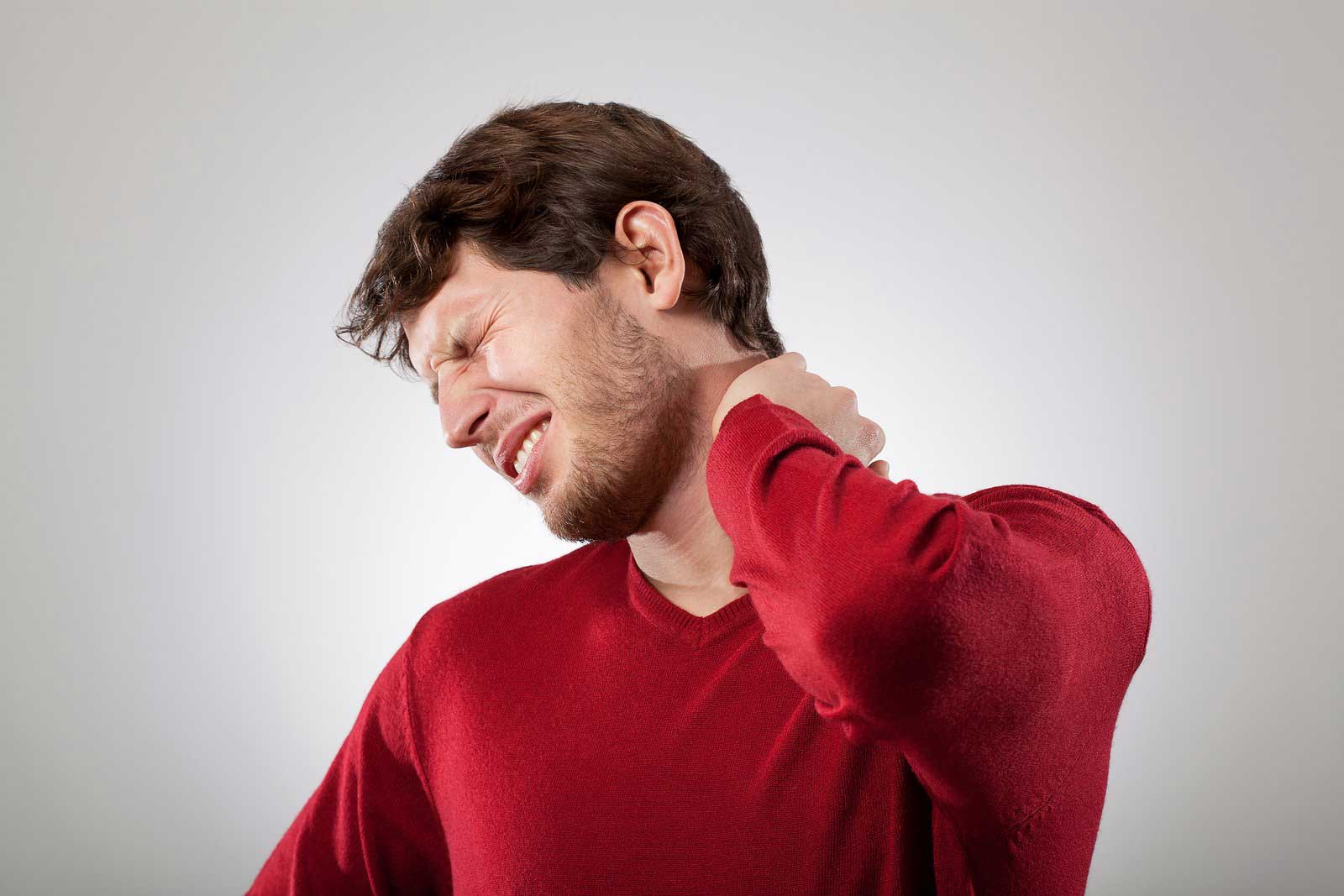
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy(CSM) is the most common cause of spinal neck dysfunction in the elderly caused by degenerative changes of the discs and facet joints in the cervical spine. Any damage to the spinal cord results in a cascade of symptoms as it transmits electrochemical signals between the brain and the body. Neck stiffness, arm pain, neck pain, and weakness of the hand and legs are common symptoms of CSM.
CSM is one of the leading causes of myelopathy and spasticity in people above 55 years old. As the name suggests- Cervical means the spinal area of the neck. Spondylotic refers to age-related spinal degeneration and myelopathy refers to damage to the spinal cord. Usually, damage to the spine occurs when the spine becomes compressed (pressure, pinching, or squeezing). The ability of nerves to communicate with other body parts is disrupted by this condition.
In simple words, CSM is damage to the cervical spine due to age-related wear and tear. The most common cause of spinal cord compression is spondylosis or spine arthritis.
If you are experiencing chronic neck pain or stiffness, we can help. Our specialist at Dallas Back Clinics specializes in non-surgical and surgical treatments. Contact us and get relief from your neck pain.

What are the causes and risk factors of cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
There are many conditions that contribute to structural damage to the spine :-
-
Bone spurs :- The body's response to osteoarthritis usually results in bone spurs. As we age, disks in the spine lose height and begin to bulge. They also lose water content and become stiffer. The vertebrae move closer as the disks lose height. When a disk collapses, the body reacts by adding extra bone, also known as bone spurs, to the disk to strengthen it. This bone spurs results in stiffening of the spine. They put pressure on the adjacent nerve roots and spinal cord, which results in pain.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis :- Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means that the condition causes the immune system of the body to attack its own tissues. The condition more precisely affects the membrane that lines the cervical spine's facet joints. As a result, this membrane swells, which limits the space that is available around the spinal cord.
-
Disc Herniation :- The spinal discs have jelly-like structures, softer inside and harder outer shells. When the outer ring wears down naturally or by traumatic injury, the softer inner material pushes against the outer rings and puts pressure on nearby nerve root endings. And results in pain and discomfort.
Disks deteriorate as we age and become more prone to herniation. Lifting, pulling, bending, or twisting motions usually result in a herniated disk.
-
Injury :- An injury to the neck such as a car accident or fall leads to myelopathy. For example, in a rear-end collision, the neck may move beyond its usual range of motion in either the direction of hyperextension (backward motion) or hyperflexion (forward motion).
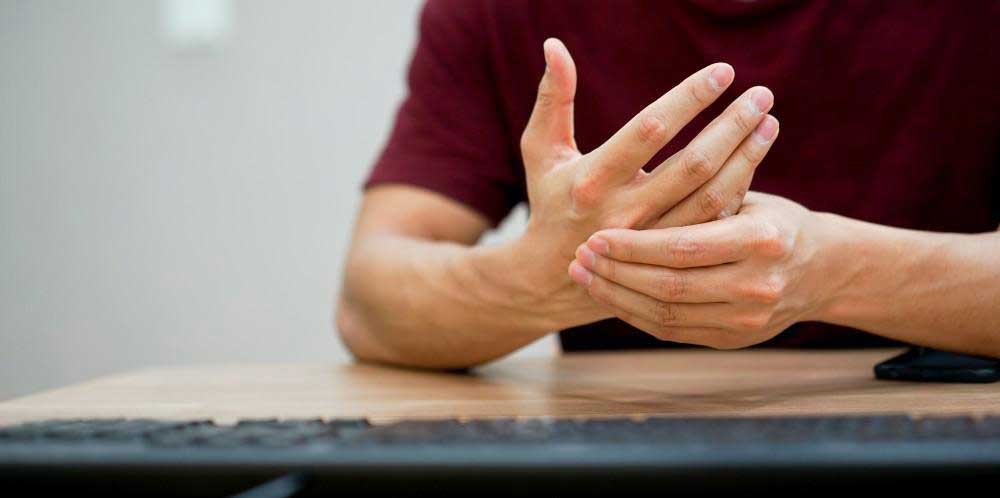
- Tingling or numbness in arms or hands.
- Weakening of the muscles that worsens over time. Patients may have trouble grasping and holding objects.
- Patients may have imbalance and walking difficulty. They feel an abnormal dissonance between the head's position in reference to the body.
- CSM results in a loss of fine motor abilities, making it difficult for patients to accomplish tasks like writing, eating, and gripping items.
- CSM causes pain and stiffness in the neck.
- Changes in your reflexes include the presence of hyperreflexia, a condition characterized by exaggerated or overactive reflexes.
- Numbness or weakness in arms or hands.
- Trouble walking.
- Atrophy is when muscles deteriorate and shrink.
-
MRI scans :- MRI scans show the body’s soft tissues and spinal cord decompression. It helps in determining whether the cause of your symptoms is soft tissue injury.
-
X-ray imaging :- X-ray shows the alignment of the vertebrae in your neck.
-
CT scans :- Computed tomography (CT) scans show a more detailed image of the spinal canal and help in determining the presence of bone spurs in the cervical spine.
-
Myelogram :- In this treatment, a contrast dye is injected into the spinal column to improve the visibility of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
-
Neck Collar :- A padded cervical collar is used to reduce neck motions, which allows the muscles to rest. However, this should be used temporarily as long-term use will weaken the neck muscles.
-
Physical Therapy :- Certain exercises increase the strength of your neck muscles. You can also maintain strength and endurance through physical therapy so that you can perform your daily activities more efficiently.
-
Medications :- The doctor may prescribe NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), oral corticosteroids, epidural injections, and narcotics to treat symptoms of CSM.

What are the symptoms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
Individual cases vary in how quickly CSM symptoms worsen. Most of the time, the symptoms appear gradually and worsen over time at a steady rate.
The following are the symptoms that CSM patient experience :-
How to diagnose cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
The doctor will ask about medical history and the symptoms and a thorough examination is done. Your doctor will probably inquire about the details of your symptoms as well as your medical history, family history, and other issues. They will look for :-
The doctor may prescribe one of the following tests if they have a suspicion that the patient has CSM :-
How is cervical spondylotic myelopathy treated?
Non-surgical options are available to relieve the symptoms of CSM which include :-
The doctor will recommend surgery if conservative measures do not relieve your symptoms. And treatment will depend on the nature and location of your CSM.

 Telehealth Visits Available
Telehealth Visits Available