Aaron Jackson
Earache Woes? Ear Infections Explained & Soothed!
Earaches are a common ailment, striking fear in both children and adults alike. That sharp, throbbing pain in your ear can be debilitating, leaving you desperate for relief. But before you reach for the strongest pain medication, understanding the culprit behind the earache – an ear infection – can empower you with knowledge and effective solutions. This article delves into the world of ear infections, exploring causes, symptoms, soothing remedies, and when to seek medical attention.
Understanding the Ouch: Demystifying Ear Infections
Ear infections occur when the middle ear cavity, located behind the eardrum, becomes inflamed and filled with fluid. This fluid buildup can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or even allergies, leading to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. While most ear infections are acute, resolving within a few days, some can become chronic if left untreated.
Here are the three main types of ear infections:
- Acute Otitis Media: The most common type, typically caused by bacteria or viruses, leading to sudden and intense ear pain.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): Fluid buildup persists in the middle ear even after an infection has cleared, potentially causing hearing loss.
- Chronic Otitis Media: A persistent or recurrent infection, often requiring long-term treatment.
Causes of Earaches: From Bacteria to Viruses and Beyond
Understanding the root cause of your earache is crucial for determining the best course of action. Here are some common culprits:
- Bacterial Infections: These are frequent causes of acute otitis media, often following upper respiratory infections like colds or allergies.
- Viral Infections: Viruses can also trigger ear infections, especially in young children.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. When this tube becomes blocked due to allergies or a cold, fluid can build up in the middle ear, leading to an infection.
- Exposure to Irritants: Swimming in polluted water or exposure to cigarette smoke can irritate the Eustachian tube and contribute to ear infections.
- Dental Issues: In rare cases, dental infections can spread to the ear, causing pain.
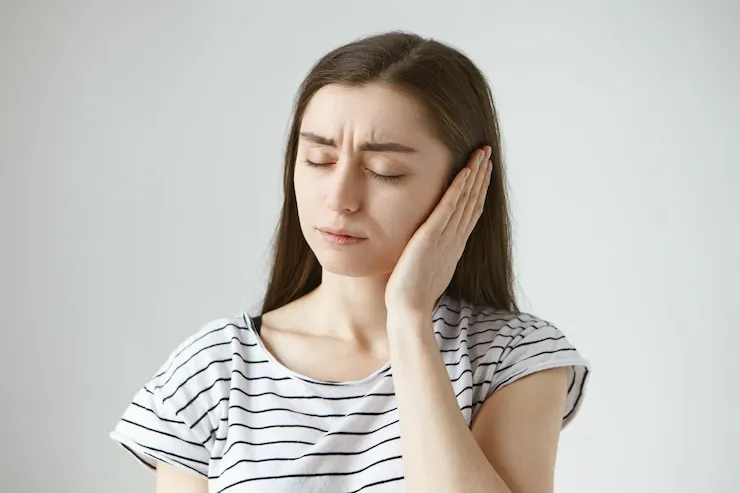

Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Ear Infections in Children and Adults
Earaches manifest differently in children and adults. Here's how to spot the signs:
In Children (who may not be able to verbalize their symptoms clearly):
- Fever
- Fussiness and crying
- Difficulty sleeping
- Pulling or tugging at the ear
- Drainage from the ear
- Loss of balance
- Difficulty hearing
In Adults:
- Ear pain, ranging from dull to sharp and throbbing
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Difficulty hearing
- Fever (less common than in children)
- Drainage from the ear
- Ringing or buzzing in the ear (tinnitus)
It's important to note that not all earaches are caused by infections. Jaw problems, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ), or even earwax buildup can mimic earache symptoms.
Soothing the Ache: Natural Remedies for Ear Infection Relief
While seeking medical attention is crucial for some ear infections, there are natural remedies you can try at home to relieve discomfort while waiting for an appointment or alongside medical treatment:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help ease pain and inflammation.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Medication: Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can offer temporary relief from pain and fever. Be sure to follow dosage instructions carefully, especially for children.
- Elevation: Elevating your head while sleeping can help with drainage and reduce pressure in the ear canal.
- Saline Drops: Using a bulb syringe with saline solution can help soften and loosen earwax buildup, which might be contributing to your discomfort.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated can help thin mucus and promote drainage.
- Rest: Adequate rest allows your body to focus on healing.
Important Note: Do not use cotton swabs to clean your ears. This can push earwax further into the ear canal and worsen the problem.
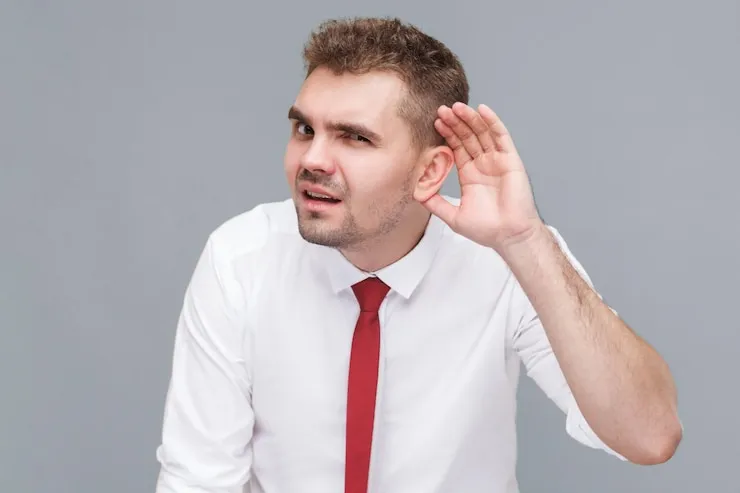

Knowing When to See a Doctor: When Earaches Need Medical Attention
While some earaches might resolve on their own with home care, others require medical attention. Here are some signs that indicate a visit to your doctor is necessary:
- Severe or persistent ear pain (lasting more than 2-3 days)
- Fever above 102°F (38.9°C)
- Drainage from the ear that is yellow, green, or bloody
- Difficulty hearing
- Dizziness or balance problems
- Facial swelling or redness
- Symptoms worsening despite

 Telehealth Visits Available
Telehealth Visits Available