Aaron Jackson
Brain Tumor: Recognizing the Warning Signs & Symptoms You Shouldn't Ignore
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells within the brain. These growths can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign). While both types can cause health problems, malignant brain tumors are typically more aggressive and require prompt treatment.
This article delves into the world of brain tumors, exploring their symptoms, signs, and the various treatment options available. By understanding these aspects, you can be better equipped to recognize potential warning signs and navigate the path towards diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Brain Tumors
Brain tumor symptoms can vary depending on the tumor's location, size, and rate of growth. Some people may experience no symptoms at all, especially if the tumor is small and slow-growing. However, some common symptoms of brain tumors include:
- Headaches: These are often the most common symptom and may be new, persistent, or worse in the morning. They may also worsen with activity and improve with lying down.
- Seizures: Seizures are sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, such as muscle jerking, convulsions, loss of consciousness, or strange sensations.
- Changes in thinking or behavior: These can include difficulty with memory, concentration, or speech. You may also experience personality changes, mood swings, or difficulty with judgment.
- Weakness, numbness, or paralysis: This can occur on one side of the body, depending on the location of the tumor.
- Balance problems or dizziness: These symptoms can be caused by tumors that affect the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance and coordination.
- Vision problems: These can include blurry vision, double vision, or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Hearing problems: Tumors can affect the nerves that control hearing, leading to hearing loss or tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
- Facial numbness or tingling: This can be a sign of a tumor that is pressing on a nerve.
- Nausea or vomiting: This can be caused by increased pressure in the skull or by irritation of the brainstem.
- Confusion and disorientation: These can be caused by tumors that affect the parts of the brain responsible for memory and thought processes.
- Fatigue or sleep problems: You may feel unusually tired or have difficulty sleeping.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of a brain tumor is crucial for successful treatment. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, it's important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation. Early diagnosis can lead to earlier treatment, which can improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Signs of Brain Tumors
In addition to the symptoms listed above, there are some other signs that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor. These include:
- Increased head circumference in infants: This can be a sign of a brain tumor in a baby.
- Difficulty swallowing: This can be caused by a tumor that is pressing on the brainstem.
- Speech problems: This can be caused by a tumor that affects the parts of the brain responsible for speech production.
- Loss of appetite or weight loss: This can be caused by a variety of factors, including the tumor itself or the side effects of treatment.
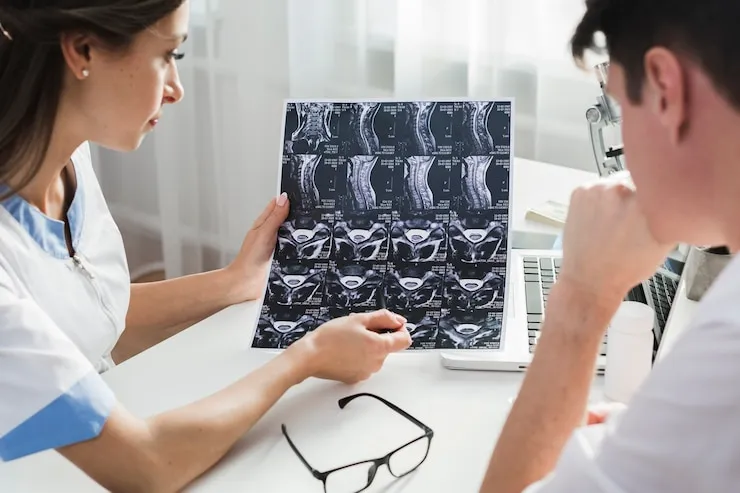
Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
If you are experiencing symptoms that suggest a brain tumor, your doctor will likely order a series of tests to determine the cause of your symptoms. These tests may include:
- Neurological examination: This is a physical examination that assesses your nervous system function, including your reflexes, coordination, and balance.
- Imaging tests: These tests can create images of your brain, such as an MRI scan or a CT scan. Imaging tests can help to identify the location and size of a tumor.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of a brain tumor. This involves taking a small sample of tissue from the tumor for examination under a microscope.
Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
There are several different treatment options available for brain tumors, depending on the type, location, and grade of the tumor. The main types of treatment include:

- Surgery: Surgery is often the first line of treatment for brain tumors. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used before or after surgery, or as a primary treatment for tumors that cannot be surgically removed.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be given orally or intravenously (through a vein).
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy drugs are designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells. They may be an option for some types of brain tumors.

 Telehealth Visits Available
Telehealth Visits Available